This is a post from the https://blog.fka.dev/blog/2025-03-25-inspecting-mcp-servers-using-cli/ about Learn how to inspect and debug Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers using command-line tools and jq. This guide shows you how to explore server capabilities and test tools directly from your terminal..
Written by Fatih Kadir Akın on March 25, 2025
---
Fatih is a passionate software developer from Istanbul, Turkey, currently leading Developer Relations at Teknasyon. He has authored books on JavaScript and prompt engineering for AI tools. With a deep enthusiasm for web technologies and AI-assisted development, he actively contributes to open-source projects and builds innovative things on GitHub. Beyond coding, Fatih enjoys organizing conferences and sharing knowledge through talks. A strong advocate for open-source collaboration, he specializes in JavaScript and Ruby (particularly Ruby on Rails). He also created prompts.chat, a platform for exploring and optimizing AI prompts for LLMs.
READ THIS POST CAREFULLY WITH ALL THE CHUNKS BEFORE RESPONDING.
This post contains explanations of some concepts in given context, code examples and instructions about the topic.
When you see a code block, analyze it and be ready to apply similar patterns. Pay attention to:
1. Code blocks marked with ```language-name - these contain example code
2. Explanatory text around the code that provides context
3. Any specific instructions or notes about implementation
4. Variable names and patterns that may need to be reused
When implementing similar code (if exists), maintain consistent:
- Naming conventions
- Code style and formatting
- Error handling patterns
- Documentation approach
The goal for the reader is to understand the concepts and be able to apply them appropriately in new situations.
Written by Fatih Kadir Akın, on March 25, 2025
---
# Inspecting and Debugging MCP Servers Using CLI and jq
While the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is primarily designed for AI assistants like Claude Desktop, Windsurf or Cursor, it's incredibly useful to be able to inspect and test MCP servers directly from the command line. In this tutorial, I'll show you how to use standard CLI tools and `jq` to interact with MCP servers, making development and debugging much easier.
## Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- An MCP server to test (you can use any from my previous tutorials)
- `jq` installed (`brew install jq` on macOS)
- Basic familiarity with JSON and command-line tools
## Understanding the MCP Protocol
MCP uses JSON-RPC 2.0 over stdio or SSE transport. For CLI testing, we'll focus on stdio transport, which means we can simply pipe JSON messages to our server's stdin and read responses from stdout.
The basic structure of an MCP request is:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "method/name",
"id": 1,
"params": {}
}
```
## Listing Available Tools
Let's start with the most basic operation: listing available tools. Here's how to do it:
```bash
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"tools/list","id":1}' | npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code | jq
```
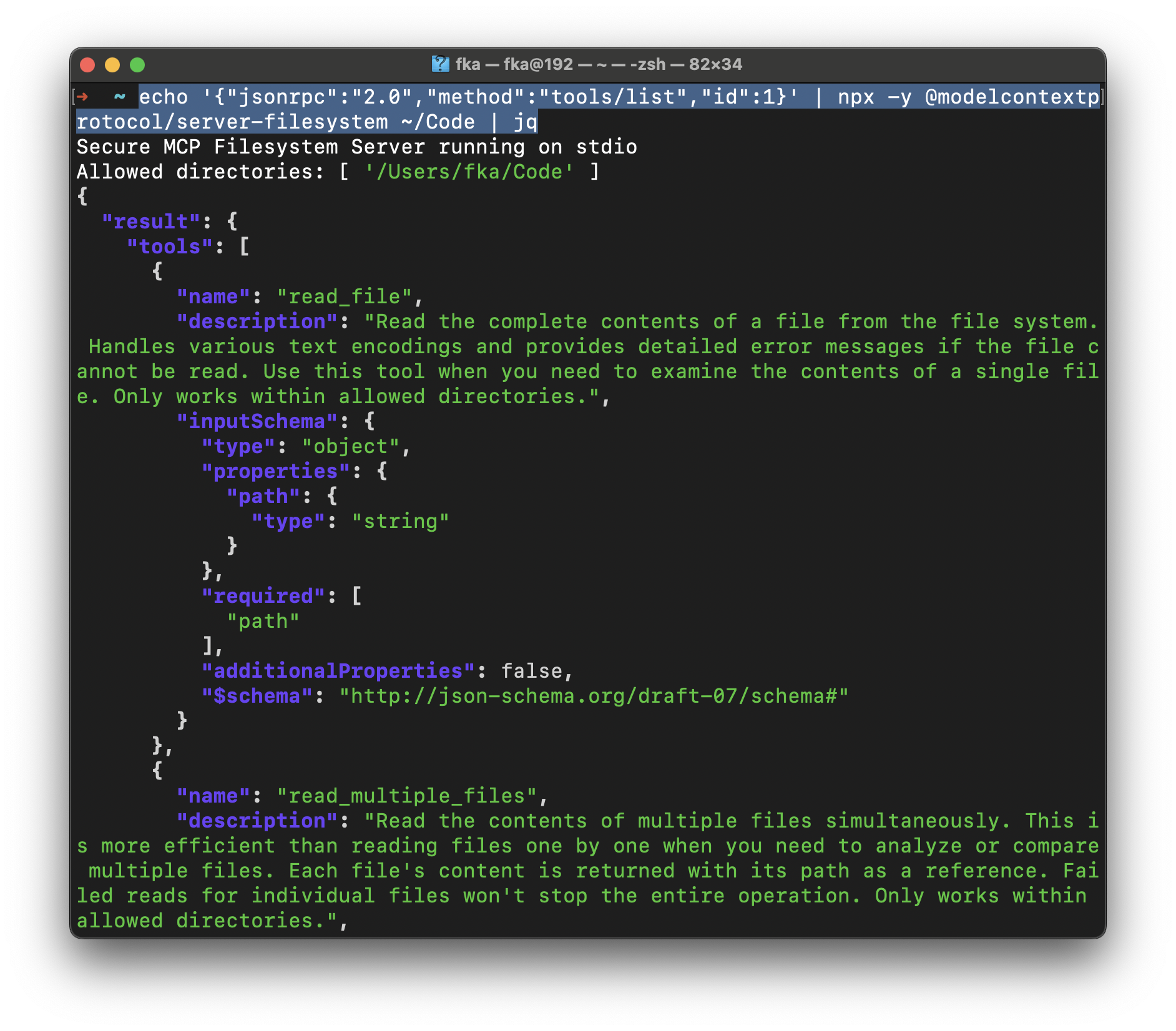
This command:
1. Uses `echo` to send a JSON-RPC request
2. Pipes it to an MCP server (in this case, the filesystem server)
3. Uses `jq` to pretty-print the JSON response
The response shows us all available tools and their input schemas. From the screenshot, we can see the server provides:
- `read_file`: For reading single files
- `read_multiple_files`: For efficiently reading multiple files at once
## Testing Individual Tools
Once you know what tools are available, you can test them directly. Here's how to test the `read_file` tool:
Here's the JSON-RPC:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "read_file",
"arguments": {
"path": "/Users/fka/Code/blog/CNAME"
}
},
"id": 2
}
```
And here's how to execute it:
```bash
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"tools/call","params":{"name":"read_file","arguments":{"path":"/Users/fka/Code/blog/CNAME"}},"id":2}' | npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code | jq
```
## Exploring Resources
MCP servers can also provide resources. List them with:
```bash
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"resources/list","id":3}' | mpc-server-exec | jq
```
## Useful jq Filters
Here are some helpful `jq` filters for working with MCP responses:
1. Get just the tool names:
```bash
... | jq '.result.tools[].name'
```
2. Get detailed info about a specific tool:
```bash
... | jq '.result.tools[] | select(.name == "read_file")'
```
3. Extract input schema:
```bash
... | jq '.result.tools[] | select(.name == "read_file") | .inputSchema'
```
4. Get call response:
```bash
... | jq '.result.content[].text'
```
## Creating Shell Helper Functions
To make testing easier, you can create shell functions for common operations. Add these to your `.zshrc` or `.bashrc`:
```bash
# List MCP tools
mcp_tools() {
local server_command=("${@}")
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"tools/list","id":1}' | "${server_command[@]}" | jq
}
# Call an MCP tool
mcp_call() {
local tool="$1"
local args="$2"
shift 2
local server_command=("${@}")
echo "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\",\"method\":\"tools/call\",\"id\":1,\"params\":{\"name\":\"$tool\",\"arguments\":$args}}" | "${server_command[@]}" | jq
}
# List MCP resources
mcp_resources() {
local server_command=("${@}")
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"resources/list","id":1}' | "${server_command[@]}" | jq
}
```
Then use them like this:
```bash
# List available tools
mcp_tools npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code
# Read a file (note the quotes around arguments)
mcp_call read_file '{"path":"/Users/fka/Code/blog/README.md"}' npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code
# List resources
mcp_resources npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code
```
Example usage with response filtering:
```bash
# Get just the content of a file
mcp_call "read_file" '{"path":"/Users/fka/Code/blog/README.md"}' npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code | jq -r '.result.content[].text'
# Get list of tool names only
mcp_tools npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code | jq -r '.result.tools[].name'
# Common error: Missing server command (will show usage)
mcp_call "read_file" '{"path":"README.md"}' # Wrong! Missing server command
# Correct usage with full command
mcp_call "read_file" '{"path":"README.md"}' npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code # Correct!
```
## Debugging Tips
1. **Validate JSON Schema**
```bash
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"tools/list","id":1}' | npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code | jq '.result.tools[].inputSchema' > schema.json
```
2. **Monitor Server Logs**
```bash
# In one terminal
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code 2>server.log
# In another terminal
tail -f server.log
```
3. **Test Error Handling**
```bash
# Try to read a non-existent file
mcp_call read_file '{"path":"/nonexistent"}' npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem ~/Code
```
## Conclusion
Command-line tools provide a powerful way to inspect and debug MCP servers. By combining standard Unix tools like `echo` and `jq` with the MCP protocol, you can:
- Explore server capabilities
- Test tools interactively
- Debug issues efficiently
- Automate testing
- Build development workflows
The next time you're building or debugging an MCP server, try these CLI techniques before integrating with Claude Desktop or other AI assistants. They'll help you understand and verify your server's behavior more quickly.
_This article was proofread and edited with AI assistance._